728x90
반응형
4. 최대 수입 스케쥴(PriorityQueue 응용문제)
설명
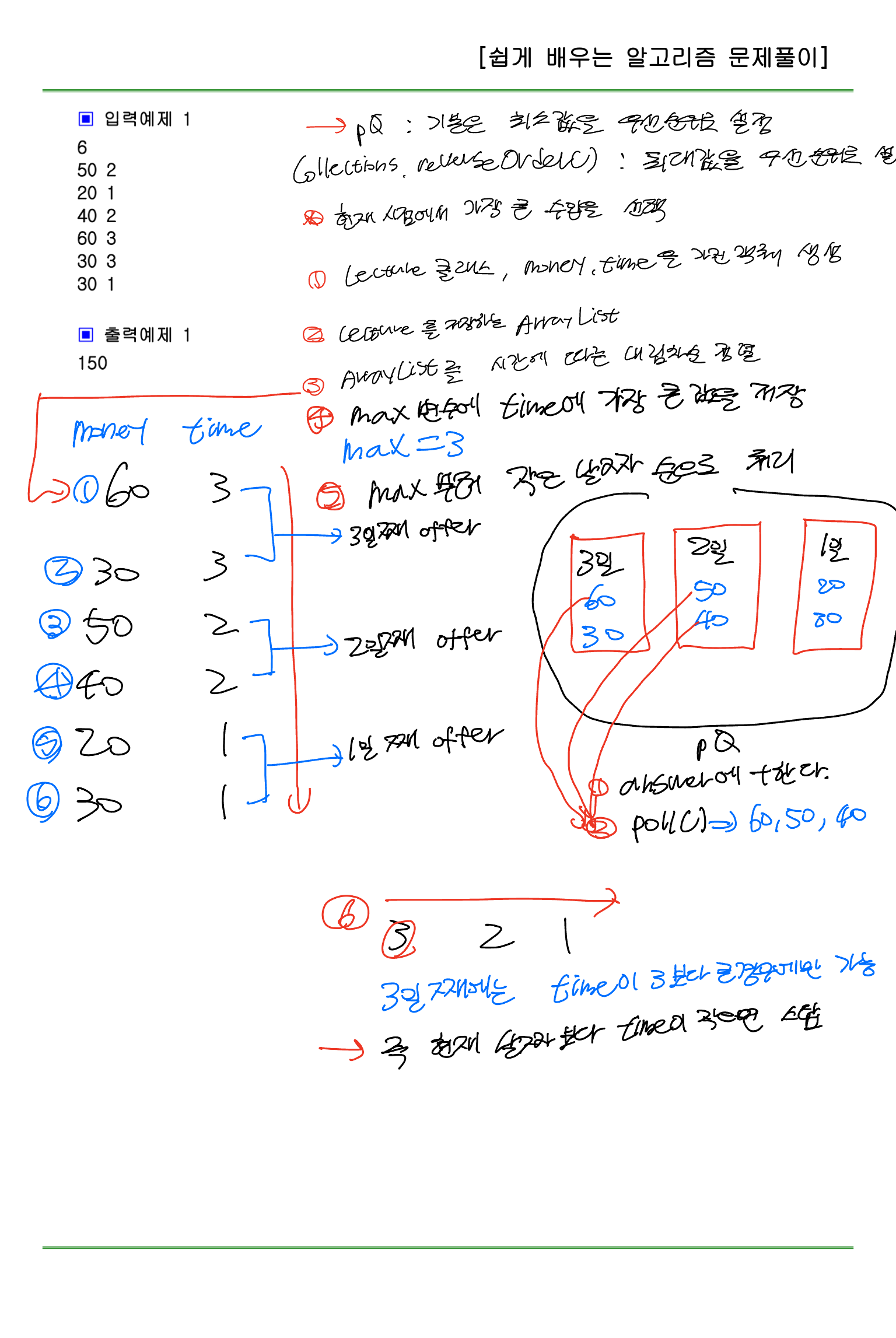
현수는 유명한 강연자이다. N개의 기업에서 강연 요청을 해왔다. 각 기업은 D일 안에 와서 강연을 해 주면 M만큼의 강연료를 주기로 했다.
각 기업이 요청한 D와 M를 바탕으로 가장 많을 돈을 벌 수 있도록 강연 스케쥴을 짜야 한다.
단 강연의 특성상 현수는 하루에 하나의 기업에서만 강연을 할 수 있다.
입력
첫 번째 줄에 자연수 N(1<=N<=10,000)이 주어지고, 다음 N개의 줄에 M(1<=M<=10,000)과 D(1<=D<=10,000)가 차례로 주어진다.
출력
첫 번째 줄에 최대로 벌 수 있는 수입을 출력한다.
예시 입력 1
6
50 2
20 1
40 2
60 3
30 3
30 1
예시 출력 1
150
import java.util.*;
class Income implements Comparable<Income> {
int money, day;
Income(int money, int day) {
this.money = money;
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Income o) {
// if(this.day==o.day)
// return o.money-this.money;
// else
return o.day - this.day;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = kb.nextInt();
int max = 0;
ArrayList<Income> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int money = kb.nextInt();
int day = kb.nextInt();
list.add(new Income(money, day));
max = Math.max(max, day);
}
System.out.println(solution(n, list, max));
}
static int solution(int n, ArrayList<Income> list, int max) {
Collections.sort(list);
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
int answer = 0;
int j=0;
// 가장 큰 날짜부터 하루씩 작아질 때
for(int i=max; i>=1; i--) {
for( ; j<n;j++) {
//리스트의 처음부터 도는데, 날짜가 i보다 작으면
if(list.get(j).day<i)
break;
//멈춘다.
else
q.offer(list.get(j).money);
//작지 않으면, 큐에 넣는다.
}
if(!q.isEmpty())answer+=q.poll();
}
return answer;
}
}
+) 세련된 풀이
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Lecture implements Comparable<Lecture> {
int money, time;
Lecture(int money, int time) {
this.money = money;
this.time = time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Lecture o) {
// if (this.time == o.time) {
// return o.money - this.money;
// }
return o.time - this.time;
//내림 차순
}
}
public class Main {
static int n, max=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int solution(ArrayList<Lecture> arr) {
//Queue<Integer> Q = new PriorityQueue<>();
//작은 값을 우선순위로
int answer=0;
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
//큰 값을 우선순위로
// Q.offer(arr);
Collections.sort(arr);
// ArrayList<Lecture> tmp=Q.poll();
//3일째부터 중복없이 가장 큰 날짜순으로 넣는 방법
int j=0;
for(int i=max;i>=1;i--) {
//가장 큰 날짜부터 하루씩 작아진다.
for(;j<n;j++) {
//리스트의 가장 큰 날짜부터 접근하기 위한 for문
if(arr.get(j).time<i){
//리스트[j번째]의 시간 -> 가장 큰 날짜가 i보다 작을 때
break;
//중복 offer를 막기 위해
}
pQ.offer(arr.get(j).money);
//해당 날짜의 money를 우선순위큐에 넣는다
}
//가장 큰 값이 max로 설정하고 max보다 작은 날짜엔 넣지 않고, max가 -1로 줄어들어서 중복 offer 방지
if(!pQ.isEmpty()) {
answer+=pQ.poll();
}
//비어있으면 poll하지 않고 끝난다.
//비어있지 않을 경우 날짜가 줄면서 계속 넣는다.
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main T = new Main();
ArrayList<Lecture> arr = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
n = kb.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int money = kb.nextInt();
int time = kb.nextInt();
arr.add(new Lecture(money, time));
if(time>max)
max=time;
//날짜중에서 가장 큰값 max
//max부터 하루씩 줄이면서 확인
}
System.out.println(T.solution(arr));
}
}
package algo2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Lecture implements Comparable<Lecture>{
public int money;
public int time;
Lecture(int money, int time){
this.money=money;
this.time=time;
}
public int compareTo(Lecture ob) {
return ob.time-this.time;
}
}
public class Test17 {
static int n,max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
static int solution(ArrayList<Lecture> arr) {
int answer=0;
//PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
//poll을 할 경우 제일 작은 값을 뽑아준다.
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
//poll을 할 경우 제일 큰 값을 뽑아준다. -> 현재 상태에서 가장 최적을 뽑는다. -> 그리디 [탐욕법]
Collections.sort(arr);
//날짜에 의해 내림차순 정렬
int j=0;
for(int i=max; i>=1; i--) {
//최대 일수에서 하루씩 줄어들면서 돈다 -> i보다 일수가 작으면 멈추고, 같거나 커야 넣는다.
for(; j<n;j++) {
//정렬된 값을 돈다.
if(arr.get(j).time<i)
break;
else
pq.offer(arr.get(j).money);
}
//i날짜에 어떤 강의를 할지 선택한다. -> 큐에서 찾아서 넣는다. -> 가장 큰 값
if(!pq.isEmpty())
answer+=pq.poll();
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
n=kb.nextInt();
ArrayList<Lecture> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int m=kb.nextInt();
int d=kb.nextInt();
arr.add(new Lecture(m,d));
if(d>max) max=d;
//날짜 중 가장 큰값을 저장 -> 제일 큰 날짜에서 하루씩 줄어들면서 돌기위해
}
System.out.println(solution(arr));
}
}
+)02.23
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
class Income{
int money;
int day;
Income(int money, int day){
this.money=money;
this.day=day;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
ArrayList<Income> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr.add(new Income(in.nextInt(), in.nextInt()));
}
Main main = new Main();
System.out.println(main.solution(arr));
}
public int solution(ArrayList<Income> arr){
int answer=0;
Collections.sort(arr, (o1,o2) -> o1.day-o2.day);
int max=arr.get(arr.size()-1).day;
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
int i=arr.size()-1;
for(;max>=1;max--){
while(i!=0){
if(arr.get(i).day<max) break;
else {
pq.offer(arr.get(i).money);
}
i--;
}
if(!pq.isEmpty()) {
answer+=pq.poll();
}
}
return answer;
}
}728x90
반응형
'Java > Java 알고리즘 인프런' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Ch.07 - Recursive] 02. 재귀함수를 이용한 이진수 출력 (0) | 2022.07.18 |
|---|---|
| [Ch.07 - Recursive] 01. 재귀함수 (0) | 2022.07.18 |
| [Ch.09 - Greedy] 03. 결혼식 ### (0) | 2022.07.16 |
| [Ch.09 - Greedy] 02. 회의실 배정 (0) | 2022.07.15 |
| [Ch.09 - Greedy] 01. 씨름 선수 (0) | 2022.07.15 |

